Women’s Health in USA
Women’s Health Matters
Despite the fact that it is generally accepted that women, especially after reaching middle age, are healthier than men, the percentage of women who consider their health to be not very good and have certain problems with it, for 2020 in the United States was about 20%. This value varies depending on ethnicity and age. American Indian and Alaska Native women have the highest number of health problems (23%), followed by Latino women. The least number of health problems is observed among women of Asian descent, as well as natives of Hawaii and the Pacific Islands.
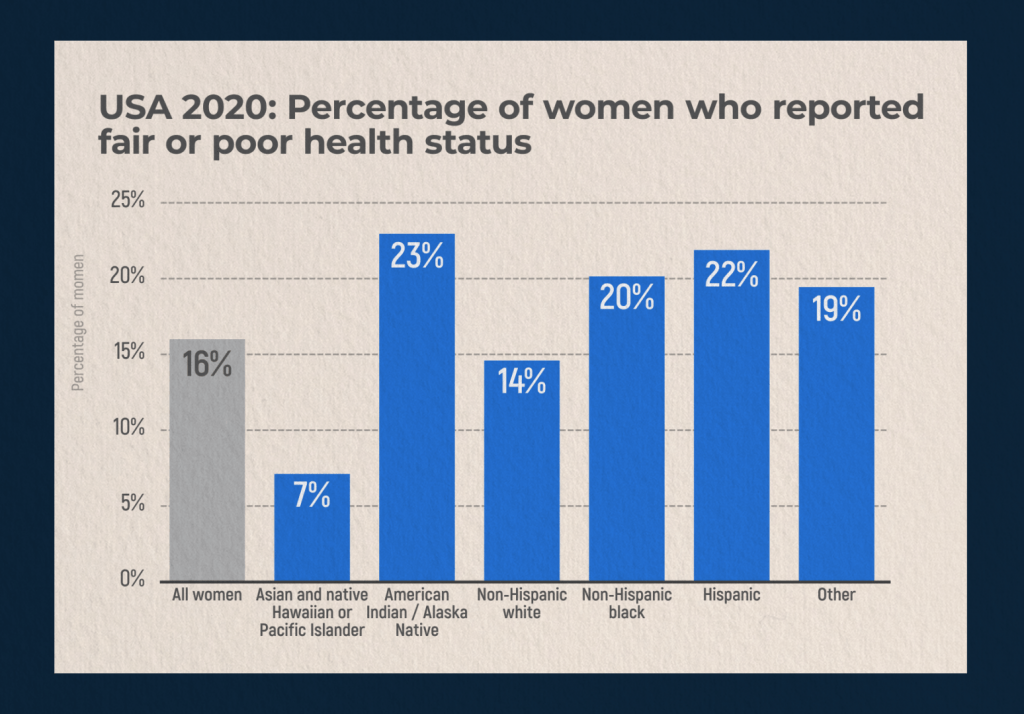
Women’s health is the most important component of the health of the nation, because it is women who are responsible for the production of healthy offspring. Of course, health of a man is also important, but a woman’s health must cope with the pressures of pregnancy and breastfeeding. Meanwhile, with the vast majority of health problems that can be classified as at least moderately serious, these processes are hampered, and both the diseases themselves and the drugs used in the treatment of these diseases can pose a danger. Finally, public opinion tends to pay more attention to men’s health problems than to women’s ones. Despite our age of emancipation and equal rights, a woman still remains in the shadows to some extent. Many scientific studies are devoted to the problems of cardiovascular diseases in men caused by bad habits, the early onset of male menopause, and psychological problems. Women’s health is given less attention. This trend needs to be reversed and more attention needs to be paid to the problems women face in the field of health, in particular, access to medical care and insurance.
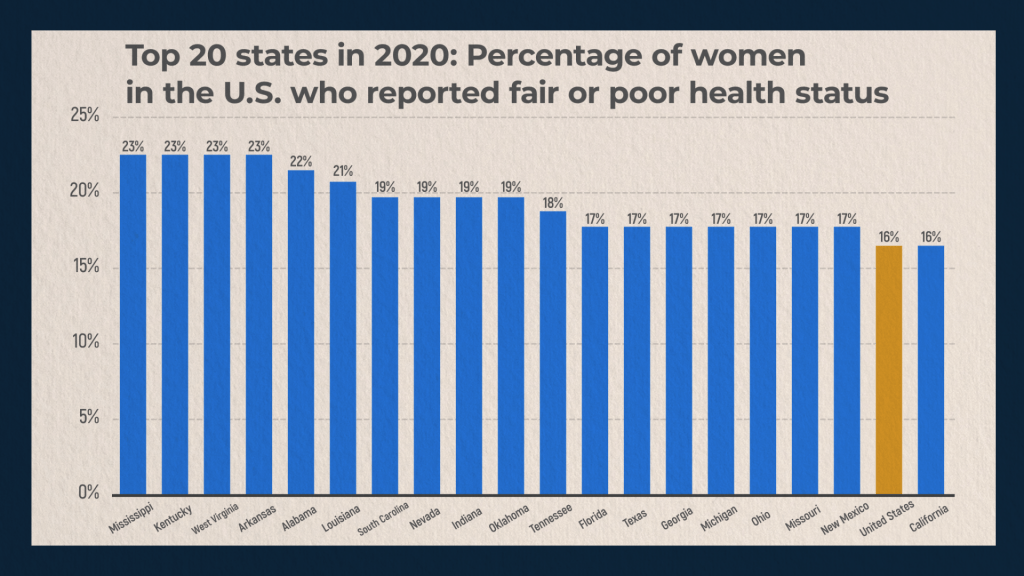
In different states of the United States, women assess their health status differently. Women have the hardest time in states such as Mississippi, Kentucky, West Virginia, Arkansas, and Alabama. Here, the number of women who reported that their health condition is fragile or poor is 22-23%. At the opposite extreme, among those who boast the strongest health, are residents of Massachusetts. Differences in the state of women’s health by state are associated with ethnicity, the material well-being of people living in different states, with the climate, with the level of accessibility and quality of medical care offered.
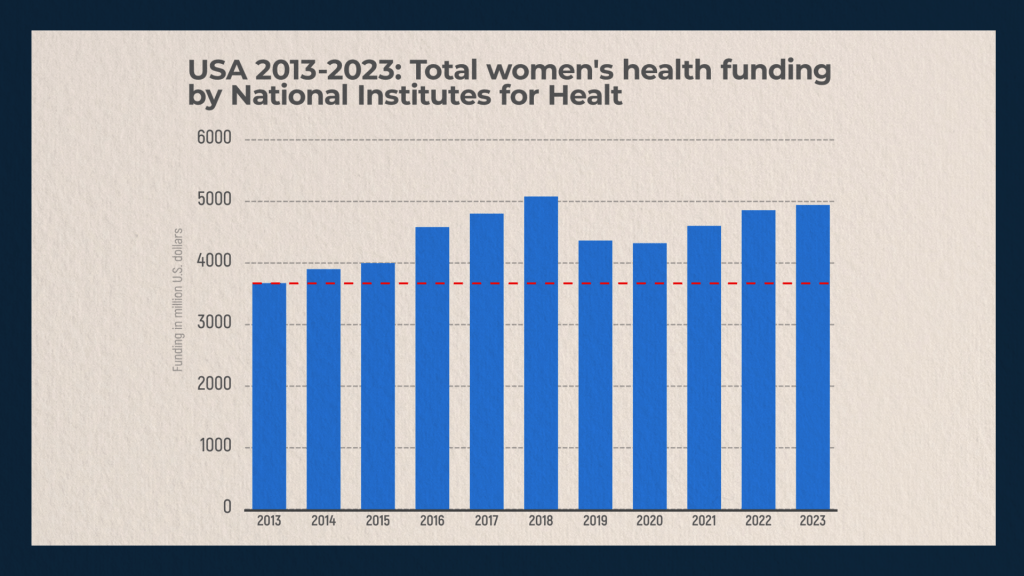
Problem Management
Fortunately, the US government is aware of women’s health related problems and is constantly dedicating quite impressive resources to address it. For example, the chart shows funding allocated by the National Institutes of Health to women’s health care from FY2013 to FY2023. As it can be seen, since 2013, spending on women’s health has risen from $3.8 billion to $5 billion. Unfortunately, this is not enough, and the gap between reality and the budget is very large, since drug prices are growing much faster than the budget allocated for women’s health care. For more information on the dynamics of drug price growth, see our article.
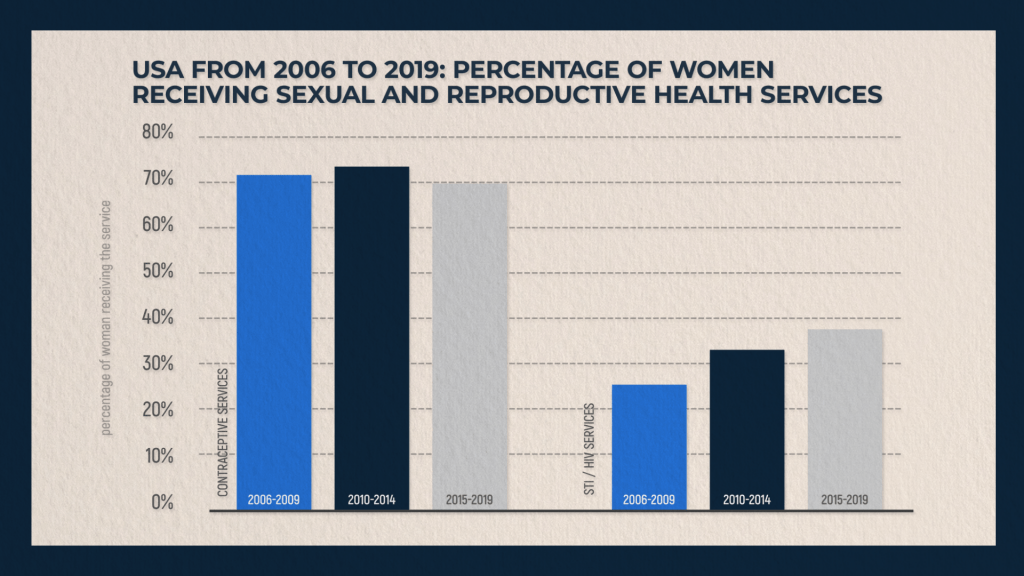
Sexual and Reproductive Health Services
While in the case of men, the focus of doctors' attention is primarily on heart and vascular diseases, as well as injuries, the most important part of women's health is sexual and reproductive health, and, accordingly, the services provided in this area. More than half of all women use services related to sexual and reproductive health. They are the most common along with the services of dentists.
As the graph shows, among women aged 15 to 44, the number of those who received treatment for sexually transmitted diseases and HIV increased from 26% to 38%. At the same time, the proportion of women who use contraceptive services remained virtually unchanged over this period. These statistics should not be viewed as evidence of an increase in the prevalence of sexually transmitted infections and HIV, but rather as evidence of an increased level of diagnosis and an increase in women’s attention to their sexual and reproductive health. American women began to visit gynecologists more often, take tests more often and, in general, take better care of their intimate health. This indicates a growing awareness in the field of sexual relations, as well as in the prevention and treatment of various pathologies and diseases.
A more detailed distribution of sexual and reproductive health services requested by women in the United States between 2006 and 2019 is as follows:
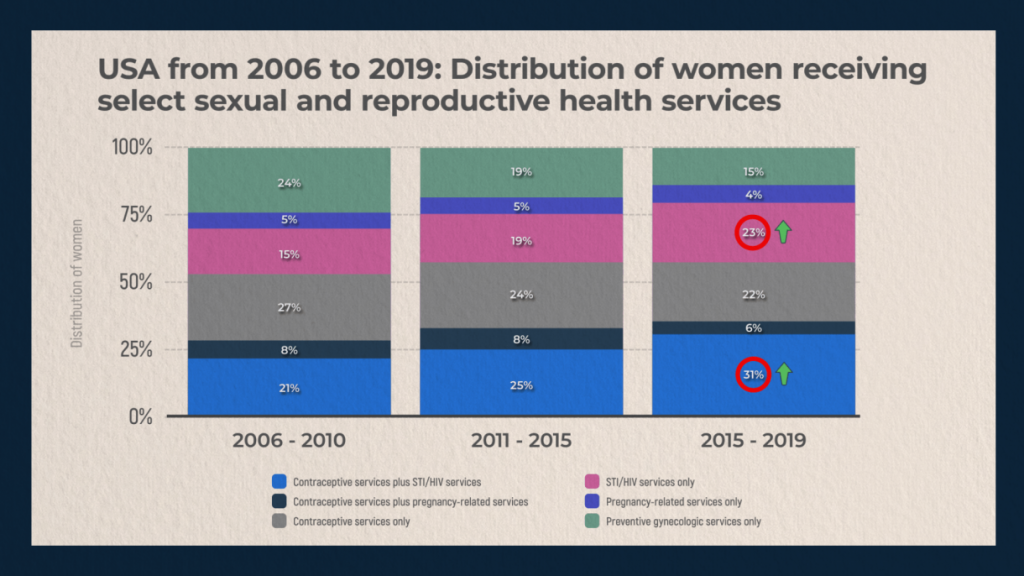
The lion’s share of all services throughout the years is occupied by contraceptive services plus sexually transmitted infections and HIV; exclusively contraceptive services; exclusively services for sexually transmitted diseases and HIV; as well as preventive gynecology services. However, the share of the latter decreased over the period from 2006 to 2019 by 9%. This value is somewhat disappointing, as it indicates that many women, due to insufficient access to medical care, don’t pay due attention to prevention of intimate diseases. This applies mainly to the poor strata of the population.
A significant factor that affects the extent to which women receive the necessary medical care, especially in the field of sexual and reproductive health, is affordable insurance plans, because it is medical insurance that determines which doctors and how many times a woman can visit, provided that these visits will be compensated from the insurance budget, if not completely, then at least partially. Since sexually transmitted diseases are rarely life-threatening, in order for women to start their treatment on time, it is necessary that medical services be available. It is also necessary to increase public awareness of the possible symptoms of diseases and when to be alert and visit a doctor.
If a person receives a serious injury, for example, a fracture, willy-nilly, he seeks medical help, which, unfortunately, cannot be said about cases of HIV or infections such as syphilis, gonorrhea and others.
Improving Women’s Health
One of the important ways to help women solve the problem of fair or poor health is to use generics, which are much cheaper and affordable for an incomparably larger number of patients. Generics are drugs that are analogues of branded ones and retain all their properties, since the active substance in generics and their prototypes is the same. Only manufacturers differ. The manufacturer of a branded drug is the pharmaceutical company that invented it. For some time (usually 20 years) the invention is under patent protection, and other companies do not have the right to copy its medicinal formula. However, after the expiration of the patent protection, any other pharmaceutical company receives the right to make their own copies of this drug. Due to the fact that generics don’t need such large-scale advertising – roughly speaking, they enjoy the glory of their ancestor – and also due to the fact that their manufacturers do not need to conduct various laboratory clinical studies, generics are available on the pharmaceutical market at a cost several times lower than the price original medicine.
In the US, you can buy both domestically produced generics and foreign-made generics, and the latter can be bought both in pharmacies based in the US and in foreign pharmacies.
Generics are especially in demand for the treatment of diseases and pathologies associated with the sexual and reproductive function of women. In particular, now there are such drugs as female Viagra (also known as Cenforce, Femalegra or Addyi) and female Cialis (Femalefil). These are drugs based on PDE-5 inhibitors. The active ingredient of female Viagra is Sildenafil citrate, and the main ingredient of female Cialis is Tadalafil. These drugs have long been considered solely as remedies for combating male erectile dysfunction, but in fact have shown their effectiveness in the treatment of female sexual dysfunction. Their effectiveness is achieved by increasing blood flow to the genital area. These drugs are not aphrodisiacs and are not able to affect the female libido. Their effect on the female body has yet to be investigated, but quite a few patients report that the quality of their sex life has improved as a result of taking these drugs. Of course, buying drugs at a price of more than $70 per pill is beyond the power of the vast majority of American women. In this regard, their generics, which we have listed above, are in great demand.
Other popular drugs used in the treatment of various women's intimate health problems include Clomid, Nolvadex, Femara.
Clomid is a drug that belongs to the group of estrogens or gestagens. It is used for scanty rare periods or the absence of menstruation; it is also indicated for the treatment of female infertility caused by endocrine disorders, the result of which is the absence of ovulation. The active ingredient in Clomid is Clomiphene. This medication is important for stimulating ovarian function in IVF protocols.
Nolvadex is an antiestrogen, an antineoplastic agent, the main indication for which is malignant tumors of the mammary glands and endometrium. The active ingredient in Nolvadex is Tamoxifen. This substance binds to estrogen receptors located on the surface of tumor cells, blocking the action of natural estrogen and disrupting the most important growth mechanisms of estrogen-dependent tumors.
Femara is a drug whose active ingredient is Letrozole. It is an aromatase inhibitor that is used in the treatment of breast cancer. It also has an antiestrogenic effect, selectively inhibiting aromatase by highly specific competitive binding to a subunit of this enzyme. This drug blocks the synthesis of estrogen in both peripheral and tumor tissue.
These drugs, especially Nolvadex and Femara, are often used in long courses and cause a serious blow to the wallet of patients. In this regard, one cannot but rejoice at the opportunity to purchase generics of all these drugs and save up to 90% of the cost. The most favorable prices are available when ordering these medicines from online pharmacies. Particular attention should be paid to Indian online pharmacies: they often have the most cost-saving offers.
